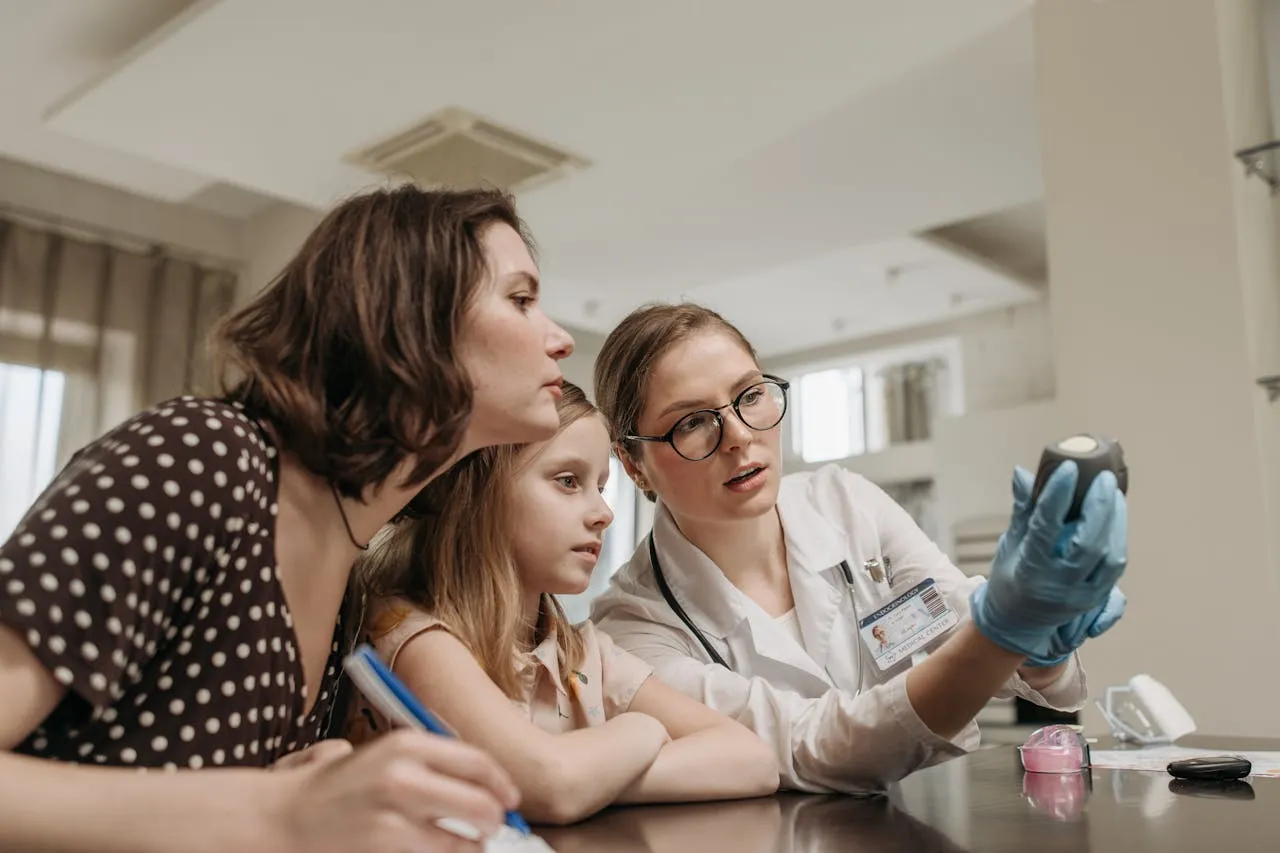
On World Children’s Day, the Global Accelerator for Paediatric Formulations Network (GAP-f) highlighted the urgent need for better access to essential medicines for children, particularly in low-resource settings. Despite their vulnerability, children often lack access to age-appropriate medications due to gaps in research, supportive policies, and timely investments.
This year, the 77th World Health Assembly (WHA) emphasized this issue by passing a resolution to accelerate progress in reducing maternal, newborn, and child mortality, aligning with Sustainable Development Goals 3.1 and 3.2. Recognized as a key platform, GAP-f is at the forefront of these efforts, driving the development and availability of quality, affordable medicines for children.
GAP-f’s Mission and Progress Report Launch
GAP-f, hosted by the WHO, fosters collaboration among stakeholders to close gaps in pediatric medicine development, prioritize unmet needs, and fast-track innovative solutions. To mark World Children’s Day, GAP-f launched its Progress Report covering its second strategic phase (2022–2024). The report details key achievements, ongoing challenges, and the impact of collaborative initiatives, offering insights to guide its next phase.
Major Milestones and Technical Contributions
Advancing Pediatric Antibiotic Approvals
In March 2023, WHO released its first-ever list of priority pediatric formulations for antibiotics to address critical gaps in treatments for children. Through collaboration with GAP-f, the Global Antibiotic Research & Development Partnership (GARDP), and PENTA, a technical consultation reviewed regulatory pathways and clinical research to accelerate access to these formulations. The resulting report outlines strategies to streamline regulatory approvals and ensure timely, equitable access to effective antibiotics for serious infections in children.
Addressing Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs)
Many NTDs disproportionately impact children, yet less than half of WHO-recommended treatments for these diseases are approved for pediatric use. A technical brief by GAP-f and WHO partners synthesizes data from the Global Observatory on Health Research and Development (GOHRD) to highlight research gaps and prioritize action for pediatric NTD treatments.
Optimizing Cancer Treatments for Children
In January 2024, GAP-f and WHO’s childhood cancer team launched the first Pediatric Drug Optimization (PADO) exercise for childhood cancers. This initiative prioritized six cancers, including low-grade glioma, with a focus on optimizing access to treatments like dabrafenib and trametinib. A second prioritization round in 2025 will assess additional therapies to improve childhood cancer outcomes.
The Path Forward
GAP-f continues to drive the pediatric medicine ecosystem forward, working with global stakeholders to address critical health challenges for children. By fostering innovation, collaboration, and evidence-based solutions, GAP-f aims to close the gap in pediatric medicine access, improving health outcomes and saving lives worldwide.
For more details, visit GAP-f’s Progress Report and related technical briefs.